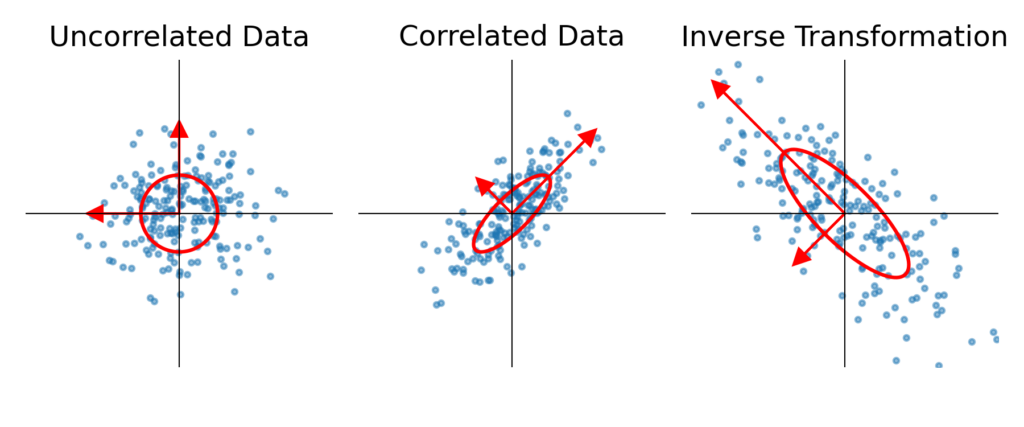
Denoising Correlation Matrices for More Stable Portfolio Optimization
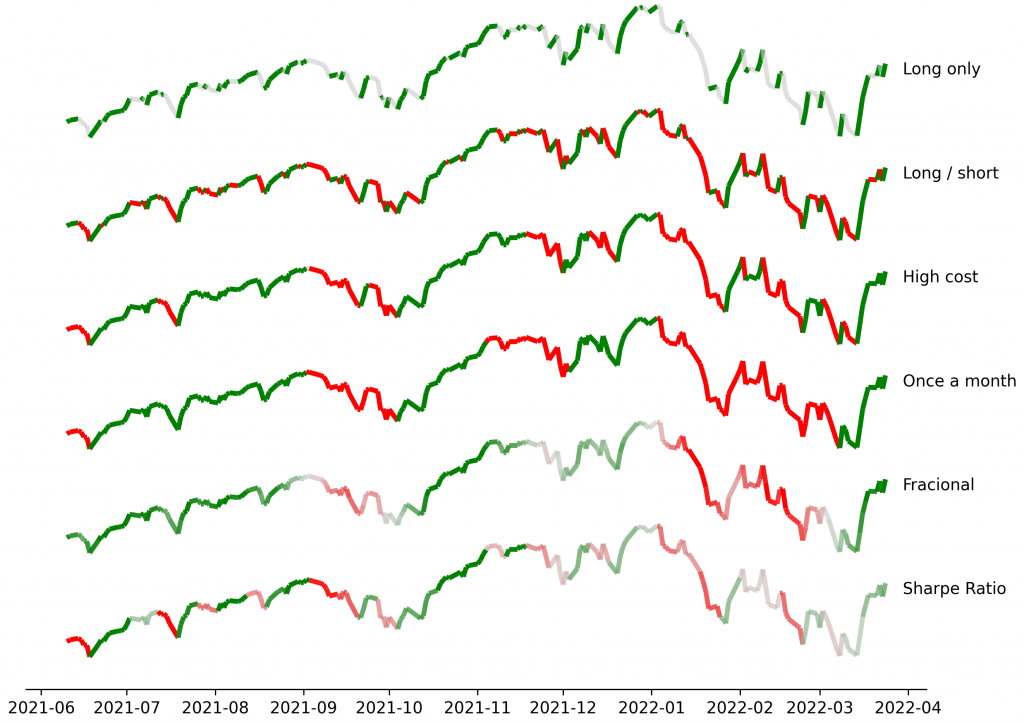
Introduction Portfolio optimization lies at the heart of asset management, guiding investment strategies from risk minimization to return maximization. Many of the most widely used allocation methods such as minimum variance, maximum Sharpe ratio, and risk parity rely on the inverse of the correlation matrix to compute optimal portfolio…
Releasing the GARCH Densities Dataset: 1,000 Trillion Simulations for Financial AI
huggingface.co/datasets/sitmo/garch_densities We’ve released a new open dataset on Hugging Face: GARCH Densities, a large-scale benchmark for density estimation, option pricing, and risk modeling in quantitative finance. Created with Paul Wilmott, this dataset contains simulations from the GJR-GARCH model with Hansen skewed-t innovations. Each row links a parameter set
<p…New release of CGMM v0.4
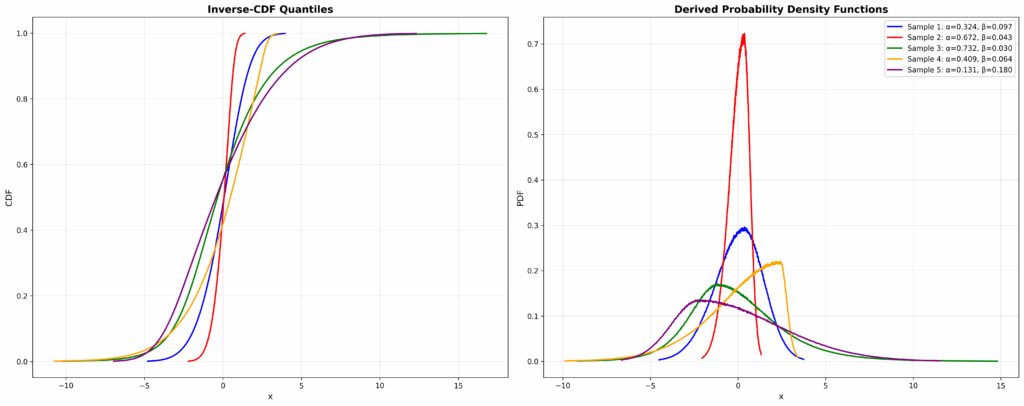
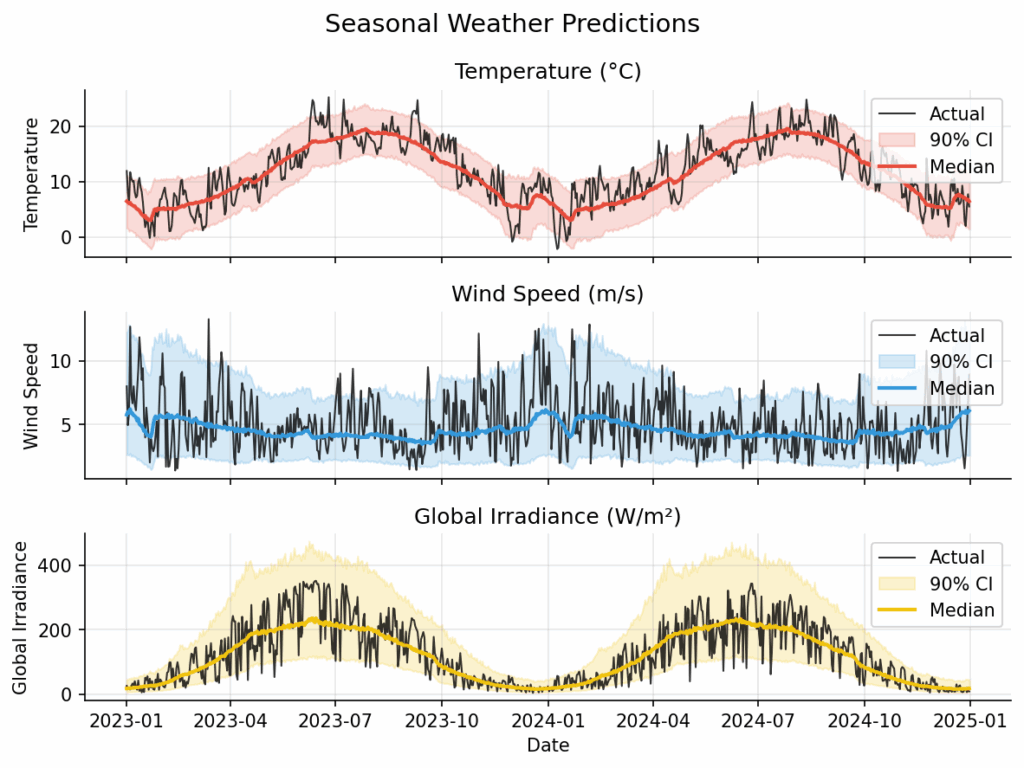
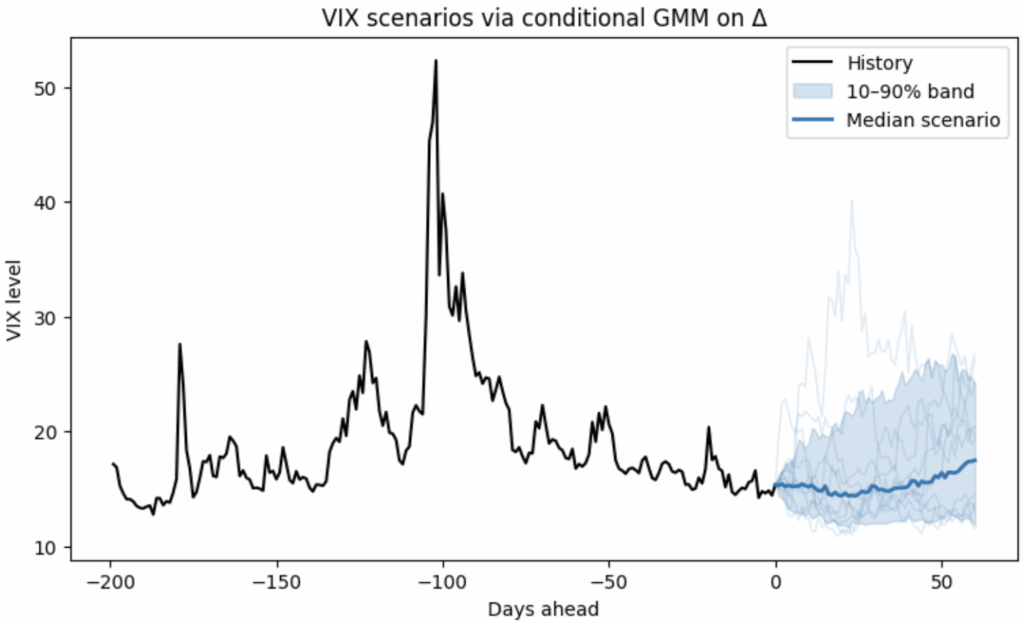
pip install cgmm We’ve just released v0.4 of cgmm, our open-source library for Conditional Gaussian Mixture Modelling. If you’re new to cgmm: it’s a flexible, data-driven way to model conditional distributions beyond Gaussian or linear assumptions. It can: Model non-Gaussian distributions Capture non-linear dependencies Work in a fully data-driven way…
New open-source library: Conditional Gaussian Mixture Models (CGMM)
pip install cgmm I’ve released a small, lightweight Python library that learns conditional distributions and turns them e.g. into scenarios, fan charts, and risk bands with just a few lines of code. It’s built on top of scikit-learn (fits naturally into sklearn-style workflows and tooling). Example usage: In the figure…
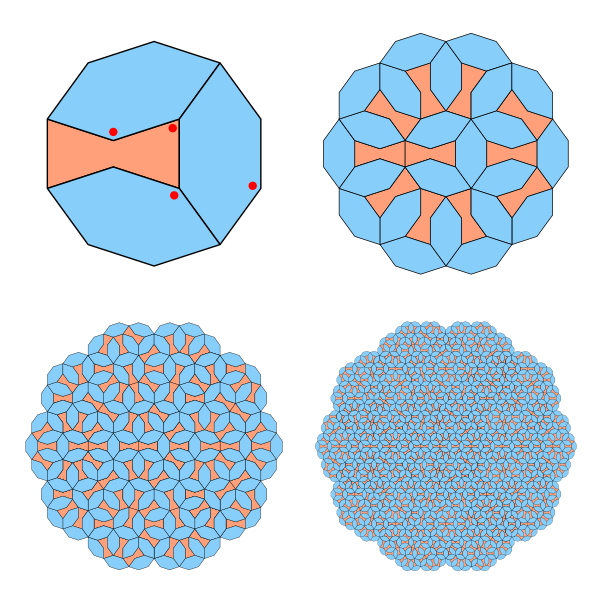
A Tiling That Never Repeats
This image below shows a tiling made from just two simple shapes, arranged in a pattern that never repeats. You can extend it as far as you like, and it will keep growing in complexity without ever falling into a regular cycle. That property alone makes it interesting, but…
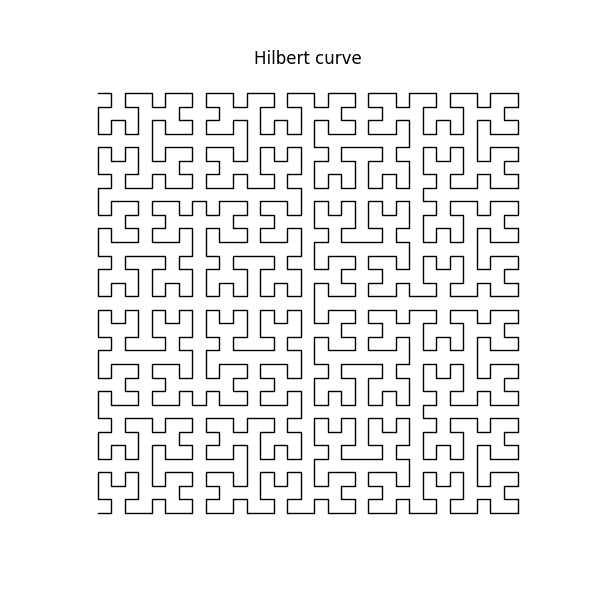
A Curve That Fills Space
Here’s a short snippet that draws the Hilbert space-filling curve using a recursive approach. It sounds counterintuitive. A curve normally has no area, it’s just a line. But a space-filling curve is a special type of curve that gets arbitrarily close to every point in a 2D square. If you…
Forecasting Current Market Turbulence with the GJR-GARCH Model
The Current Market Shake-Up Last week, global stock markets faced a sharp and sudden correction. The S&P 500 dropped 10% in just two trading days, its worst weekly since the Covid crash 5 years ago. Big drops like this remind us that market volatility isn’t random, it tends to…
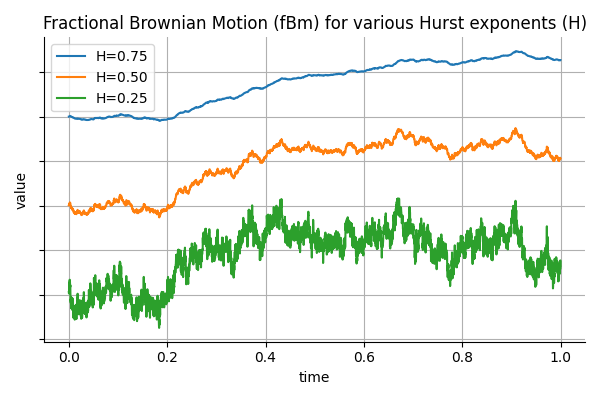
Using Fractional Brownian Motion in Finance: Simulation, Calibration, Prediction and Real World Examples
Long Memory in Financial Time Series In finance, it is common to model asset prices and volatility using stochastic processes that assume independent increments, such as geometric Brownian motion. However, empirical observations suggest that many financial time series exhibit long memory or persistence. For example, volatility shocks can persist…
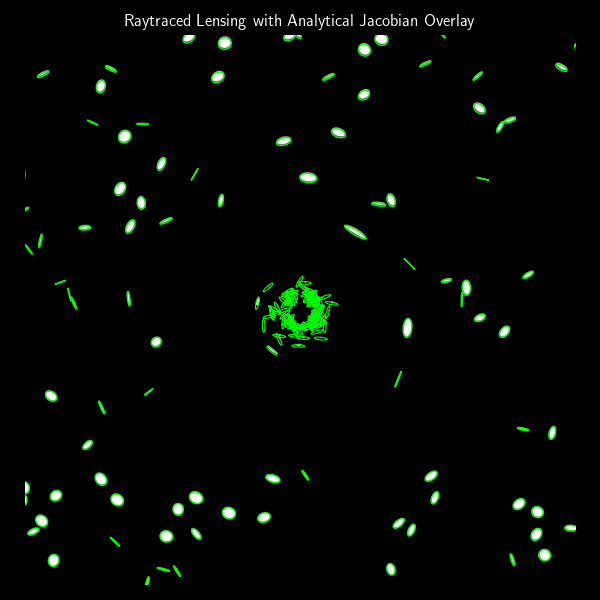
Lensing and Ellipses: How Gravitational Fields Stretch Background Galaxies
In the previous post, we built a simple gravitational lens raytracer that simulates how an image would be distorted when seen through a point-mass gravitational lens. That approach was fully numerical: we traced rays from each pixel and observed how they bent. But if we’re working with small, elliptical…
A Simple Gravitational Lens Raytracer from Scratch
Gravitational lensing is one of the most beautiful predictions of general relativity.When a massive object, like a galaxy or black hole, lies between a distant light source and an observer, the gravitational field bends the path of light rays, distorting and duplicating the image of the background object. In…
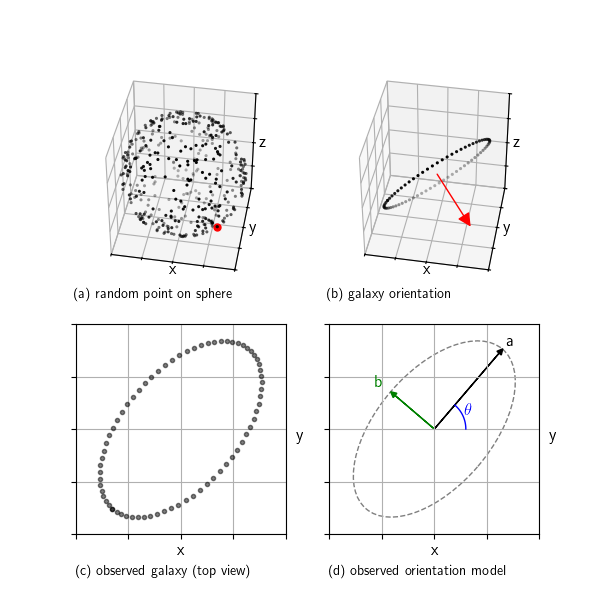
The Visible Shape of Random Galaxies: What You Get When You Project a 3D Disk
When we look at galaxies through a telescope, we see them as ellipses. But real galaxies are 3D disks randomly oriented in space. This post shows how we can simulate that: we start with a random orientation, project a flat disk into the 2D image plane, and extract the…
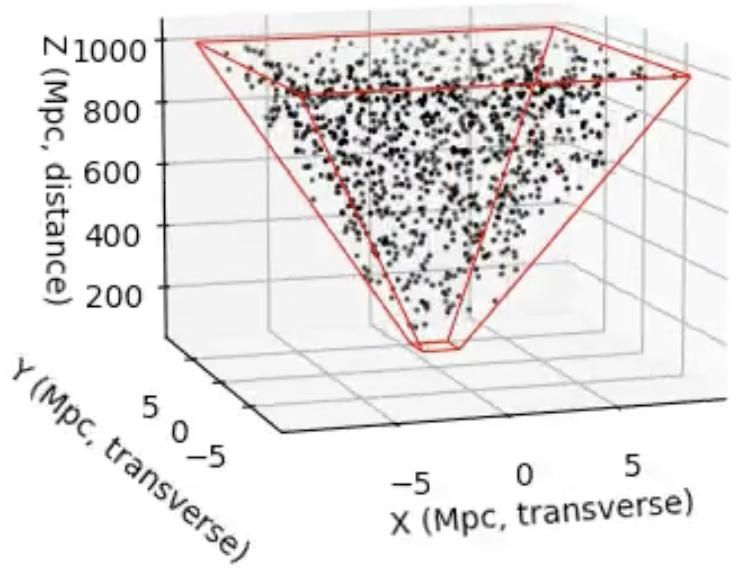
How to Sample the 3D Universe You See in an Image
When we look at an astronomical image, we see a 2D projection of a 3D universe. But suppose we want to simulate the distribution of galaxies behind that image, for example, to generate synthetic data, test detection algorithms, or check if real galaxy distributions statistically deviate from what we’d…
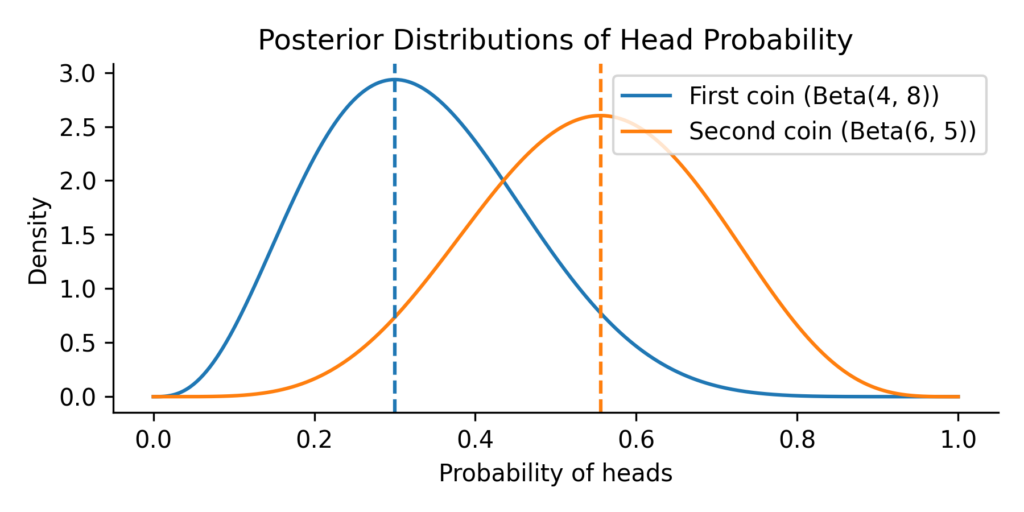
The Odds of Outshining: When One Coin Beats Another
Imagine you’re comparing two trading strategies. One has made a handful of successful trades over the past month, while the other shows a different success pattern over a slightly shorter period. Both show promise, but which one truly performs better? And more importantly, how confident can we be in…
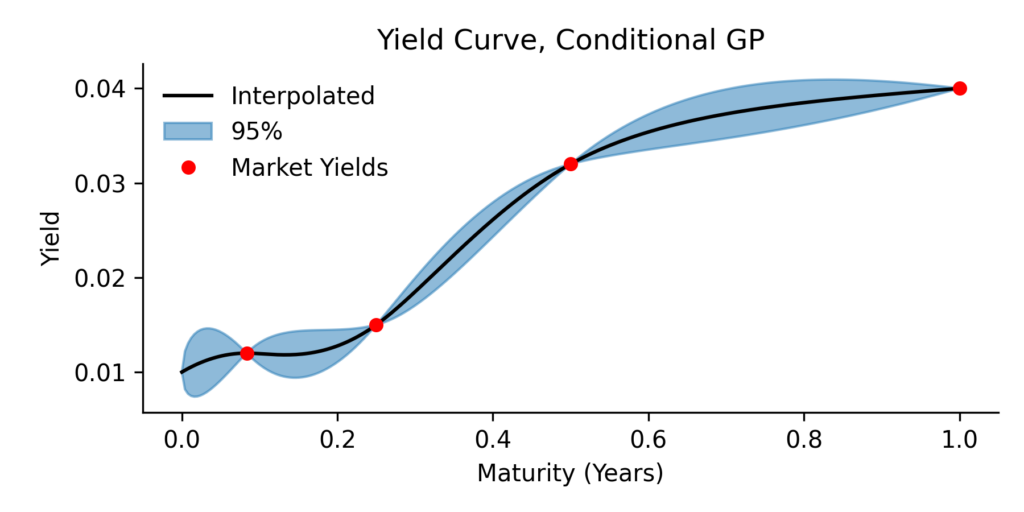
Yield Curve Interpolation with Gaussian Processes: A Probabilistic Perspective
Here we present a yield curve interpolation method, one that’s based on conditioning a stochastic model on a set of market yields. The concept is closely related to a Brownian bridge where you generate scenario according to an SDE, but with the extra condition that the start and end…
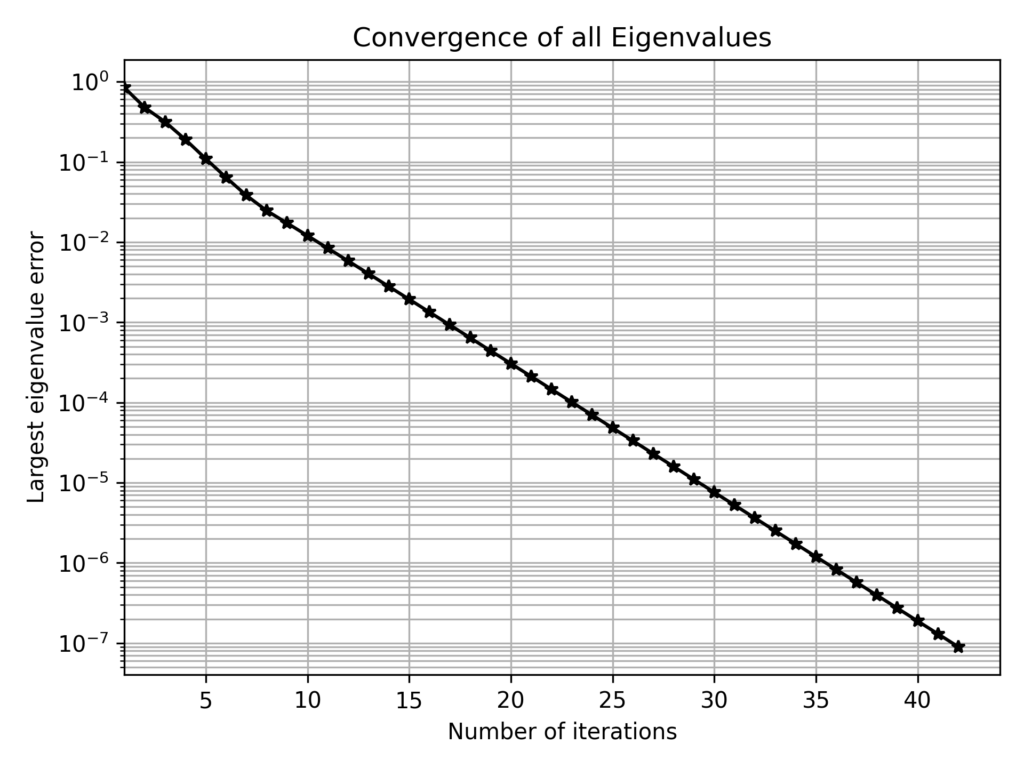
Building Correlation Matrices with Controlled Eigenvalues: A Simple Algorithm
In some cases, we need to construct a correlation matrix with a predefined set of eigenvalues, which is not trivial since arbitrary symmetric matrices with a given set of eigenvalues may not satisfy correlation constraints (e.g., unit diagonal elements). A practical method to generate such matrices is based on…
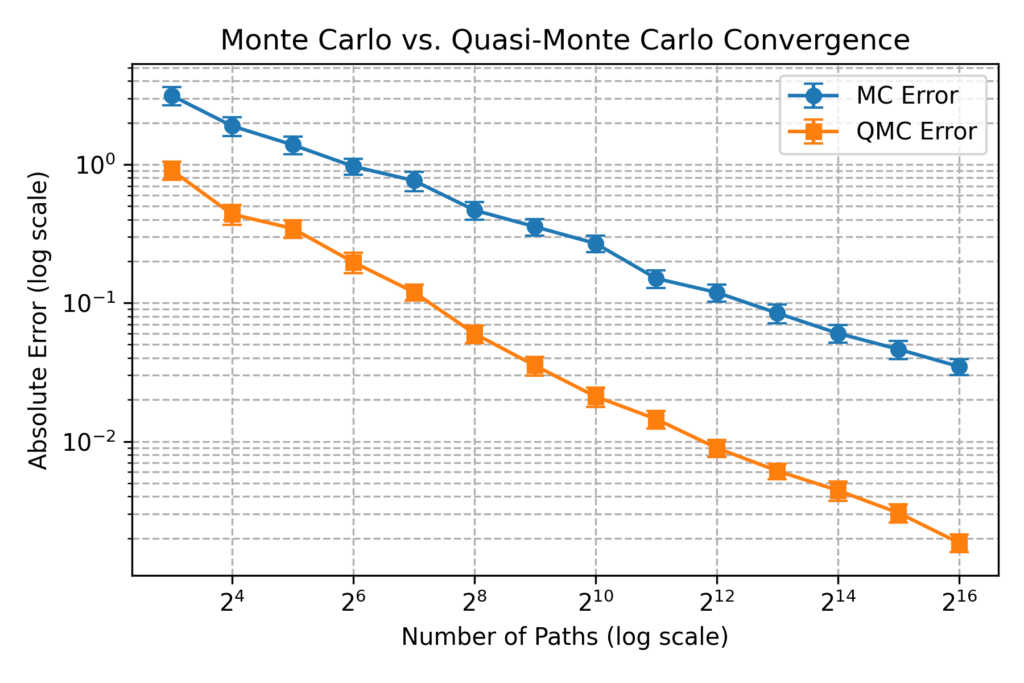
Faster Monte Carlo Exotic Option Pricing with Low Discrepancy Sequences
In this post, we discuss the usefulness of low-discrepancy sequences (LDS) in finance, particularly for option pricing. Unlike purely random sampling, LDS methods generate points that are more evenly distributed over the sample space. This uniformity reduces the gaps and clustering seen in standard Monte Carlo (MC) sampling and…
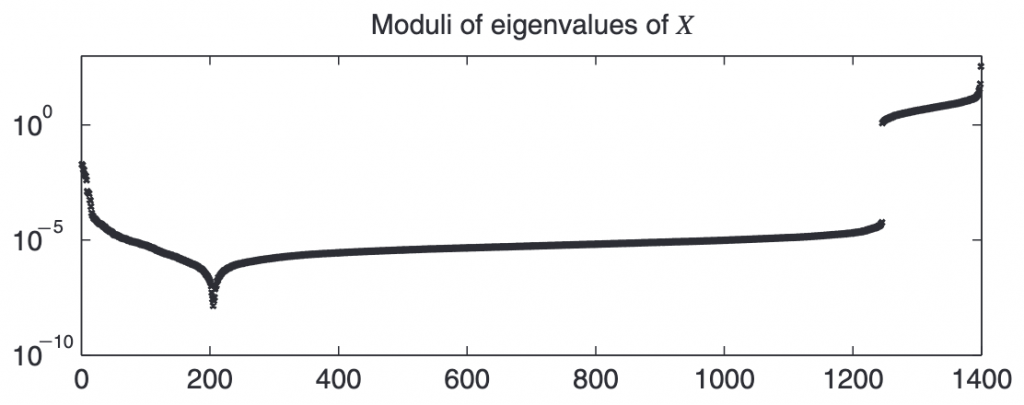
Finding the Nearest Valid Correlation Matrix with Higham’s Algorithm
Introduction In quantitative finance, correlation matrices are essential for portfolio optimization, risk management, and asset allocation. However, real-world data often results in correlation matrices that are invalid due to various issues: Merging Non-Overlapping Datasets: If correlations are estimated separately for different periods or asset subsets and then stitched together, the…
Optimal Labeling in Trading: Bridging the Gap Between Supervised and Reinforcement Learning
When building trading strategies, a crucial decision is how to translate market information into trading actions. Traditional supervised learning approaches tackle this by predicting price movements directly, essentially guessing if the price will move up or down. Typically, we decide on labels in supervised learning by asking something like: “Will…
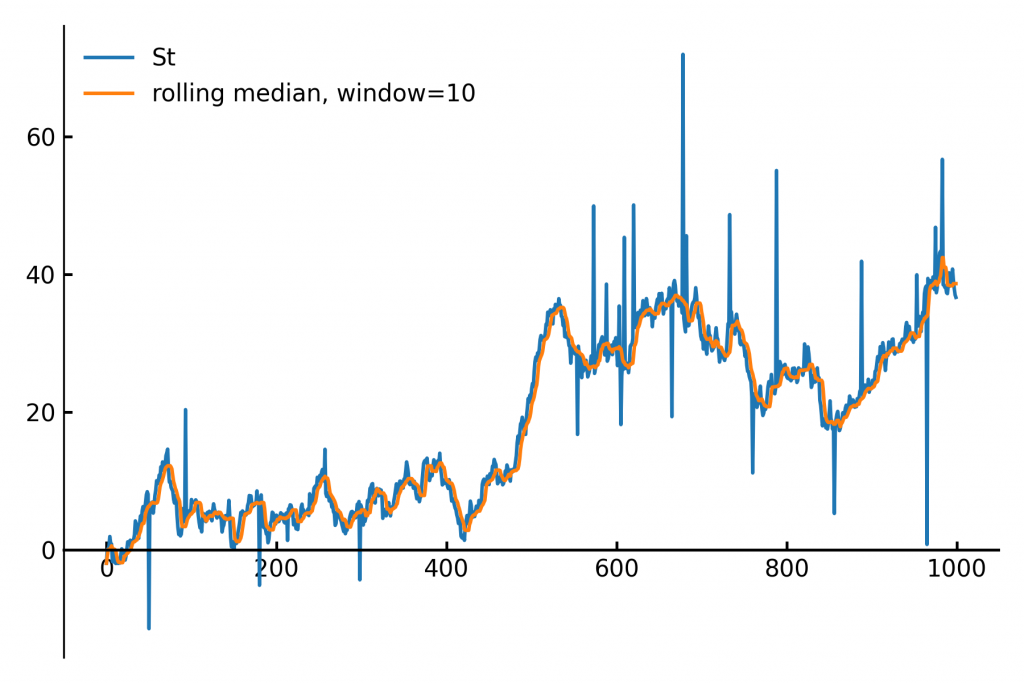
Efficient Rolling Median with the Two-Heaps Algorithm. O(log n)
Calculating the median of data points within a moving window is a common task in fields like finance, real-time analytics and signal processing. The main applications are anomal- and outlier-detection / removal. Fig 1. A slow-moving signal with outlier-spikes (blue) and the rolling median filter (orange). A naive implementation…
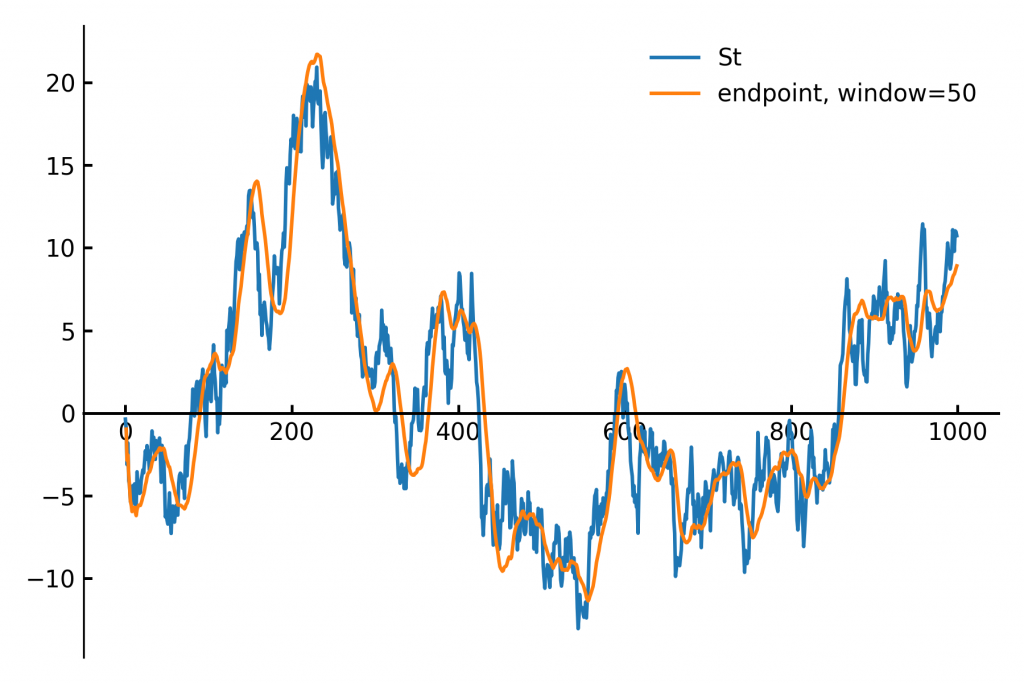
Fast Rolling Regression: An O(1) Sliding Window Implementation
In finance and signal processing, detecting trends or smoothing noisy data streams efficiently is crucial. A popular tool for this task is a linear regression applied to a sliding (rolling) window of data points. This approach can serve as a low-pass filter or a trend detector, removing short-term fluctuations…
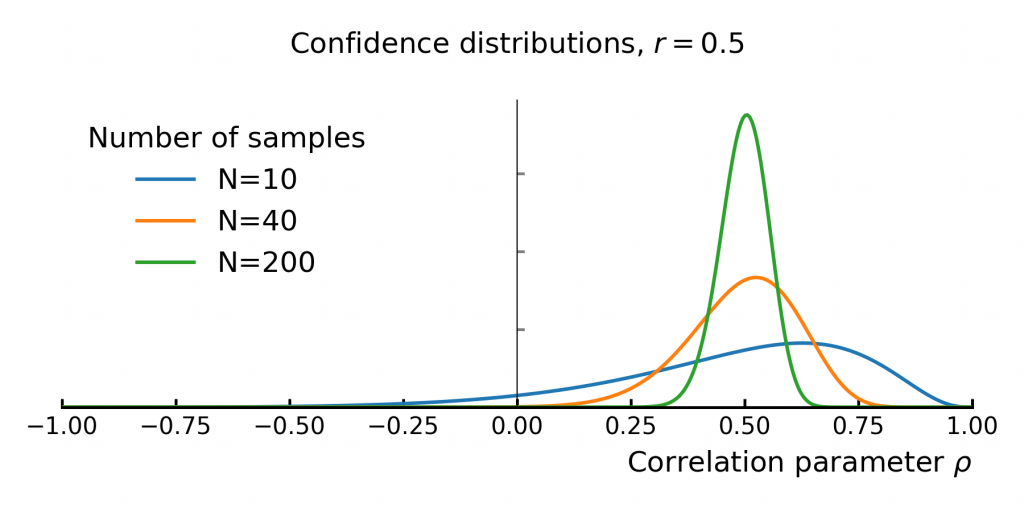
Understanding the Uncertainty of Correlation Estimates
Correlation is everywhere in finance. It’s the backbone of portfolio optimization, risk management, and models like the CAPM. The idea is simple: mix assets that don’t move in sync, and you can reduce risk without sacrificing too much return. But there’s a problem—correlation is usually taken at face value,…
Can we measure president Bush’s heart rate when he was told about the 9/11 attack?
This is a fun project me and my son did over the weekend. I’ve always wondered what was going on in president Bush’s mind right after he was informed about the 9/11 attack. Using a technique called Eulerian Video Magnification we were able to estimate his heart rate, and compare…
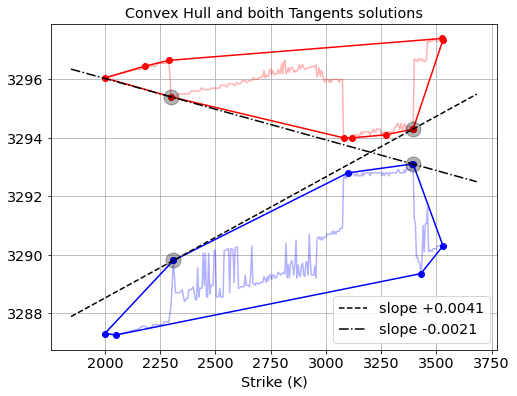
Extracting Interest Rate Bounds from Option Prices
In this post we describe a nice algorithm for computing implied interest rates upper- and lower-bounds from European option quotes. These bounds tell you what the highest and lowest effective interest rates are that you can get by depositing or borrowing risk-free money through combinations of option trades. Knowing…
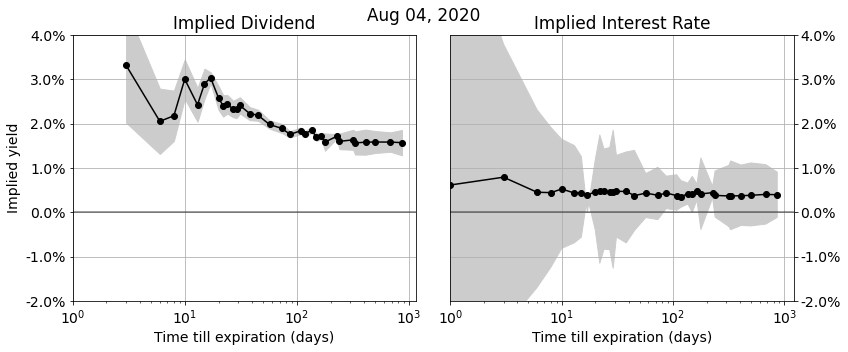
Recovering Accurate Implied Dividend and Interest Rate Term-Structures from Option Prices
In this post we discuss the algorithms we use to accurately recover implied dividend and interest rates from option markets. Implied dividends and interest rates show up in a wide variety of applications: to link future-, call-, and put-prices together in a consistent market view de-noise market (closing) prices…